Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeb) - Rare Earth:
Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB) magnets belong to the Rare Earth category and have been commercially available since the mid-1980s. Their popularity has increased significantly owing to their exceptionally high Maximum Energy Product, which denotes superior magnetic strength. Additionally, these magnets are offered in a diverse array of shapes, sizes, and grades, providing versatile solutions across numerous industrial and technological applications.
(NdFeB) magnets are produced using several manufacturing techniques, including sintering, compression bonding, injection moulding, and extrusion. Among these methods, sintering yields magnets with the highest magnetic energy product, reaching up to 48 MGOe (Mega Gauss Oersteds).

In contrast, bonded magnets, which are typically produced through compression bonding or injection moulding, exhibit a lower maximum energy product, generally up to 10 MGOe. It is important to note that the vast majority of NdFeB magnets are anisotropic, meaning they possess a preferred magnetic orientation and can only be effectively magnetised along this designated direction.
Typically, neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets require magnetising fields of approximately 30 kilo-Oersted (kOe) to achieve full magnetic saturation. These magnets, however, exhibit a susceptibility to corrosion when exposed to humid or moist environments, which can adversely affect their performance and longevity.
To mitigate corrosion risks, various protective surface treatments are employed. These include coatings such as liquid epoxy, dry epoxy, and metal platings. Common metal plating options consist of nickel, zinc, tin, phosphor, silver, or gold, either individually or in combination, applied through processes such as electroplating or spray coating. Epoxy resin coatings may also be used to provide an additional barrier against moisture ingress and environmental degradation.
The selection of an appropriate surface treatment method is critical to ensuring the durability and operational reliability of NdFeB magnets in challenging environmental conditions.
Bonded NdFeB magnets are manufactured by combining rapidly quenched Nd-Fe-B powder with a plastic resin binder, subsequently forming the magnets through compression moulding with epoxy resin or injection moulding using nylon.
Injection moulding offers a distinct advantage in producing highly complex geometries and thin-walled components, enabling intricate designs that would be challenging to achieve by other methods. Conversely, compression moulded magnets are typically restricted to simpler shapes due to process limitations; however, they benefit from a comparatively higher density. This increased density translates into superior magnetic strength relative to injection moulded counterparts, making compression moulding the preferred choice when maximising magnetic performance is critical.
Bonded NdFeB magnets exhibit lower magnetic energy properties when compared to their sintered NdFeB counterparts. Nonetheless, bonded NdFeB magnets offer superior dimensional accuracy and allow for the manufacture of complex geometries that may be challenging to achieve with sintered variants. Typically, bonded NdFeB magnets do not require additional finishing processes after production, which can streamline manufacturing timelines. To enhance durability and protect against corrosion, the surfaces of these magnets are commonly treated with protective coatings such as epoxy resin or nickel plating. These surface treatments ensure the longevity and reliability of the magnets in various applications.
Note: Additional Neodymium Iron Boron grades, including bonded versions, are available, contact sales.
Typical Magnetic Performance For Sintered NdFeB Magnet
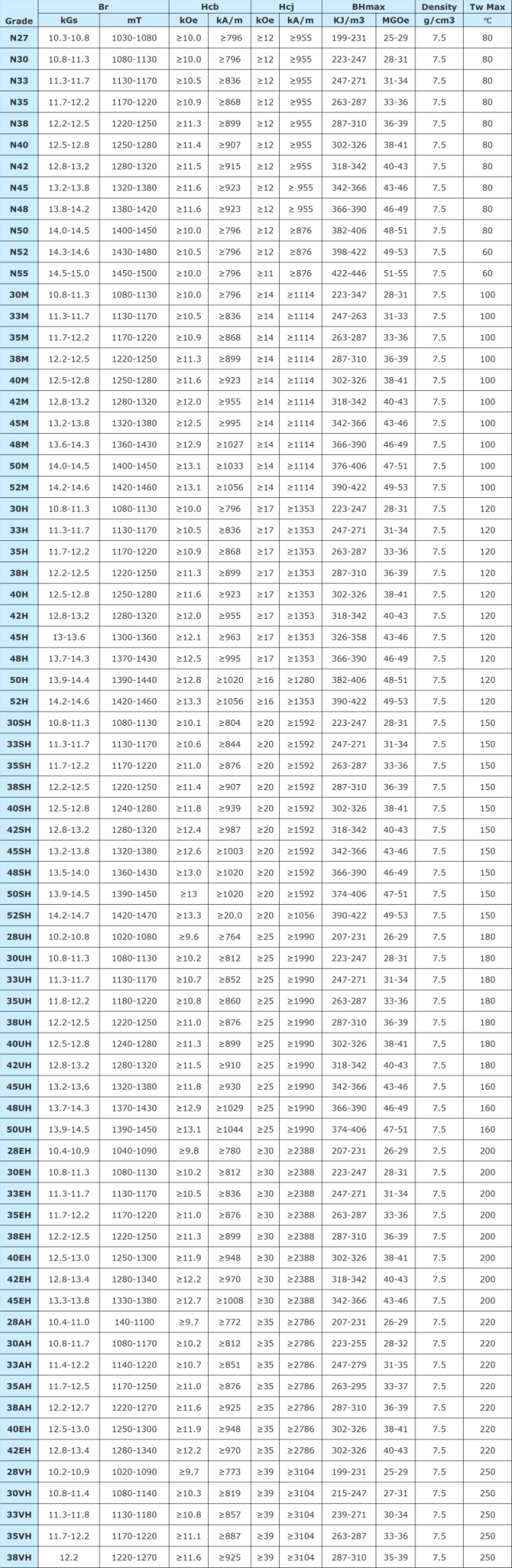
Typical Magnetic Performance For Sintered NdFeB Magnet - PDF

